
Johnson distributed newsletters, flyers, maps, and other promotional Under his leadership, over the next three decades, the Flat Earth Society grew in size from a few members to about 3,000. President of the International Flat Earth Research Society of AmericaĪnd Covenant People's Church in California. Shenton's library from Shenton's wife, established and became the When he added most of Shenton's library to the archives of the Science Fiction Foundation which he helped to establish. Little evidence of any activity on his part until after Shenton's death, Lecturer, to become president of the Flat Earth Society, but there is In 1969, Shenton persuaded Ellis Hillman, a Polytechnic The society also took the position that the Apollo Moon landings were a hoax staged by Hollywood, a position also held by others not connected to the Flat Earth Society. However it was not until the advent of manned spaceflight that Shenton managed to attract wide publicity, being featured in The New York Times in January and June 1964, when the epithet "flat-earther" was also slung across the floor of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom in both directions. "It's easy to see how a photograph like that could fool the untrained Sphere rather than flat, the society was undaunted Shenton remarked: This was just before the launch of the first artificial satellite,Īnd when satellite images taken from outer space showed the Earth as a The emphasis on religious arguments was less than in the predecessor īecause of Shenton's interest in alternative science and technology, Society and ran it as "organizing secretary" from his home in Dover, in Britain. International Flat Earth Society as a successor to the Universal Zetetic In 1956, Samuel Shenton, a signwriter by trade, created the After World War I, the movement underwent a slow decline. Later it achieved some notoriety by being involved in a scam involving dental practices. Photographed the effect, sparking a correspondence in the magazine English Mechanic with several counter-claims. In 1901, she repeated Rowbotham's Bedford Level Experiment and A flat Earth journal, Earth: a Monthly Magazine of Sense and Science, was published between 1901–1904, edited by Lady Blount. The society published a magazine entitled The Earth Not a Globe Review, and remained active well into the early part of the 20th century. In confirmation of the Holy Scriptures, based on practical scientific Whose objective was "the propagation of knowledge related to Natural Cosmogony Sir Walter de Sodington Blount, established a Universal Zetetic Society, Īfter Rowbotham's death, Lady Elizabeth Blount, wife of the explorer
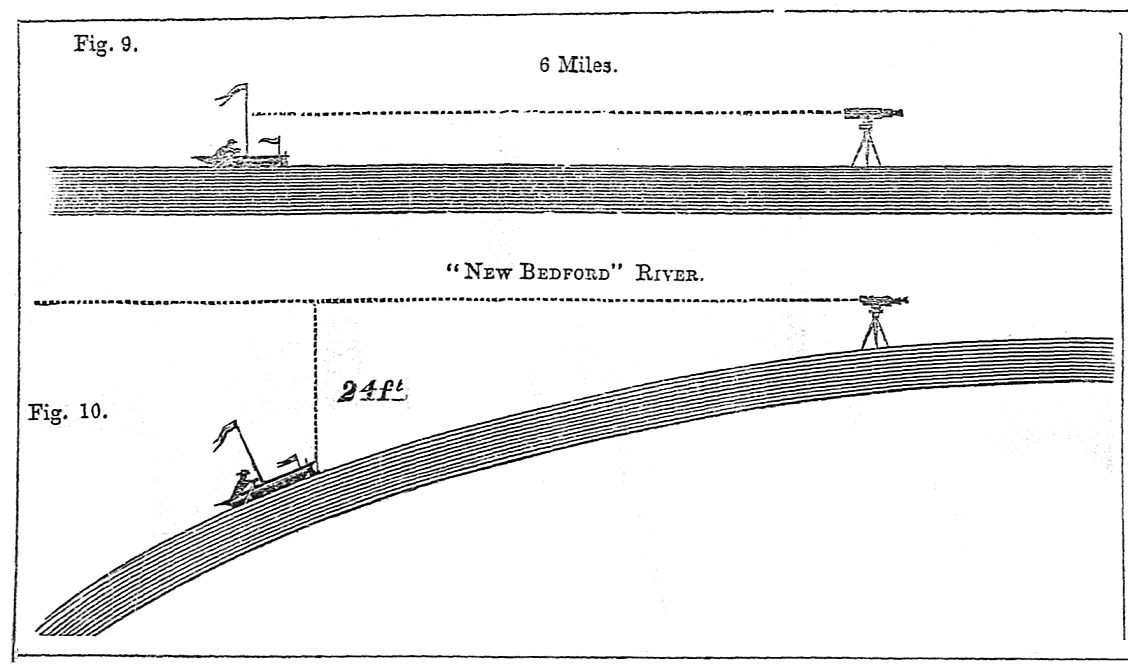
He also edited " The Zetetic and Anti-Theorist: a monthly journal of practical cosmography". Superintendent of Baltimore public schools. Rowbotham created a Zetetic Society in England and New York, shipping over a thousand copies of Zetetic Astronomy.Ĭouncil members in New York included the US Consul to China and the One such debate, involving the prominent naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace, concerned the Bedford Level experiment (and later led to several lawsuits for fraud and libel). Rowbotham and his followers, like William Carpenter who continued his work, gained attention by engaging in public debates with leading scientists of the day. Not be set aside for a system based solely on human conjecture". That the earth was flat and immovable and this essential truth should Which argued that the "Bible, alongside our senses, supported the idea He also published a leaflet entitled " The inconsistency of Modern Astronomy and its Opposition to the Scriptures!!" According to Rowbotham's system, the earth is aįlat disc centred at the North Pole and bounded along its southern edgeīy a wall of ice ( Antarctica), with the sun and moon 3,000 miles (4,800 km) and the "cosmos" 3,100 miles (5,000 km) above earth. Based on his incorrect interpretation of experiments on the Bedford Level, Rowbotham published a 16-page pamphlet, called "Zetetic Astronomy", which he later expanded into a 430-page book, Earth Not a Globe,Įxpounding his views.

Modern hypotheses supporting a flat Earth originated with English inventor Samuel Rowbotham (1816–1884). By the early Middle Ages, it was widespread knowledge throughout Europe that the Earth was a sphere.

Aristotle was one of the first Greek thinkers to propose a spherical Earth in 330 BC. Proposed the idea that the Earth was a sphere, or at least rounded in Until about the 4th century BC, when the Ancient Greek philosophers The idea that the Earth was flat was typical of ancient European cosmologies


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
